FERC grants Sayreville Power waiver, allowing mothballed units to compete in PJM auction
The decision hinges on Sayreville reaching an emissions offset agreement with the state of New Jersey before Sept. 1.

The decision hinges on Sayreville reaching an emissions offset agreement with the state of New Jersey before Sept. 1.

The decisions enable two mothballed power plants totaling over 300-MW of capacity to potentially return to service in PJM, addressing capacity needs.

Shifting fuel mix sees solar, storage, and hybrid or thermal projects dominate interconnection queue, surpassing wind.
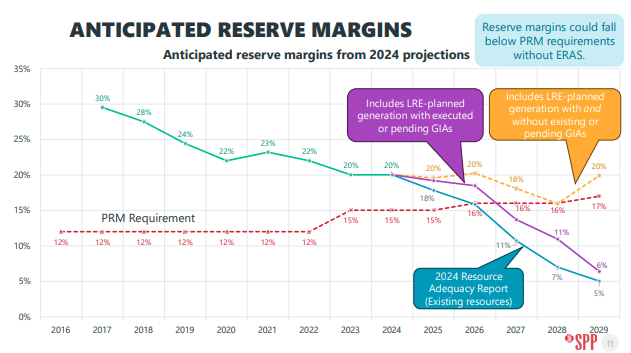
SPP projects a 17 GW capacity shortfall by 2030, necessitating the accelerated study and integration of new projects to meet resource adequacy and reliability needs.
FERC Chairman Mark Christie emphasized the unsustainable pace of dispatchable generation retirements and the need for additional capacity.
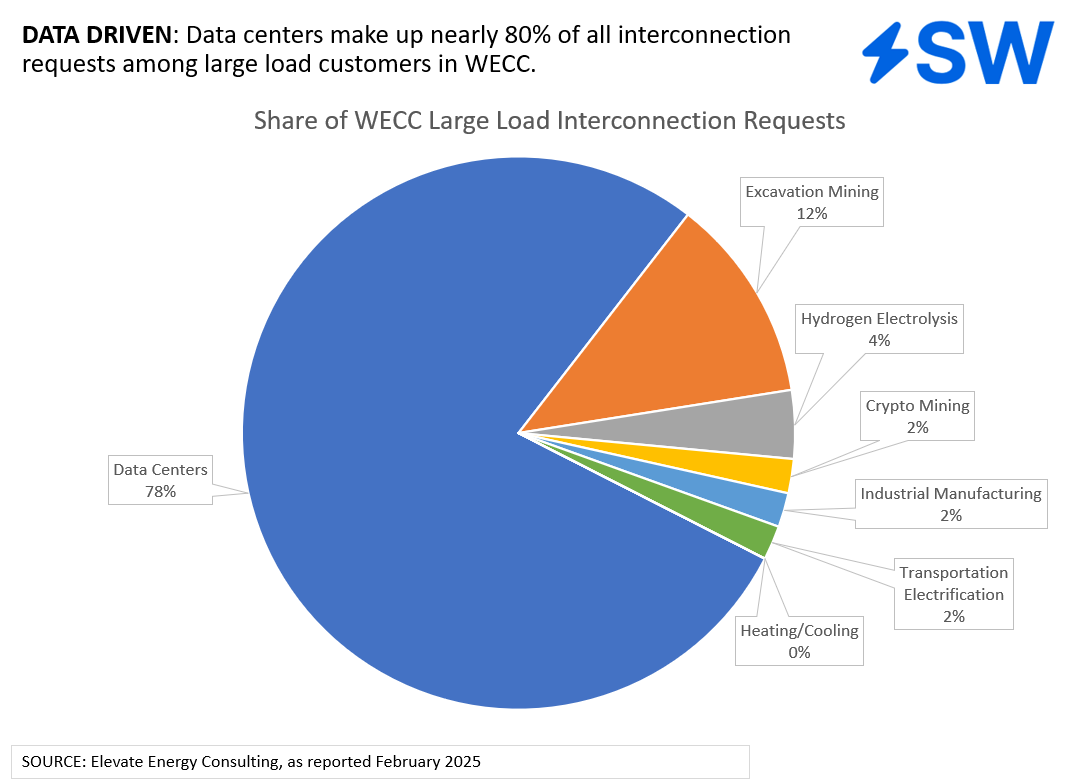
Data centers in the Western Interconnection are dominating the grid connection queues, accounting for nearly 80% of total requests from large load customers.
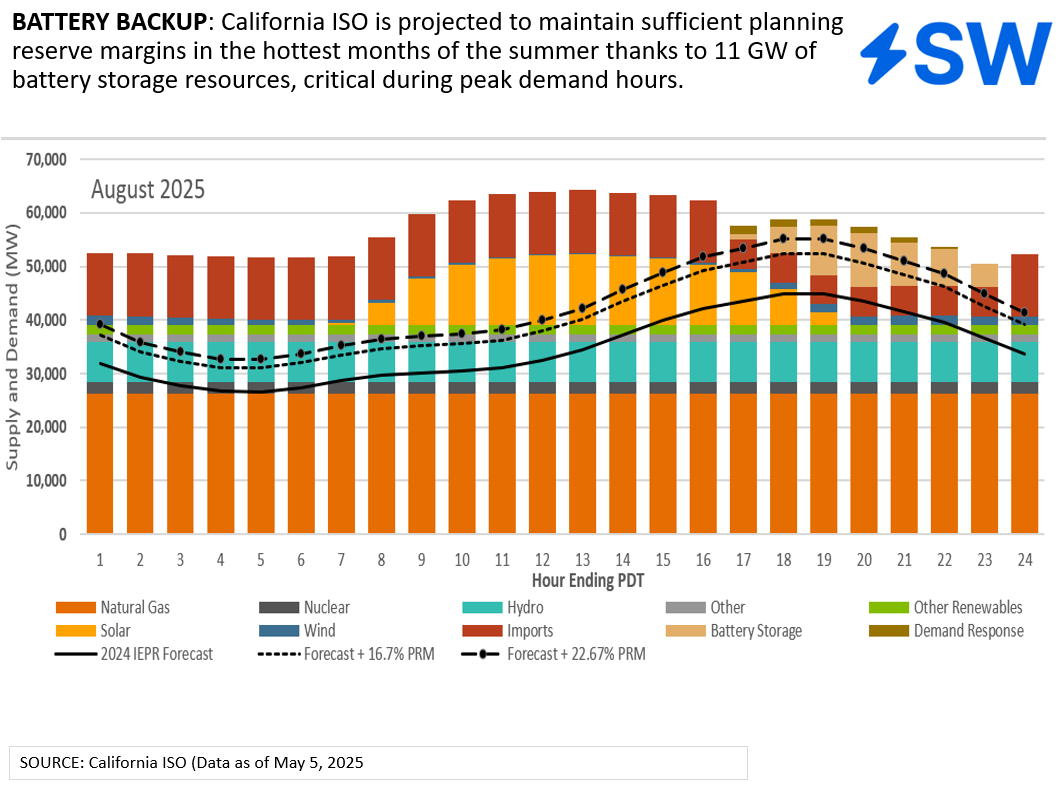
Larger capacity reserves and over 11 GW of battery storage resources are putting the California grid manager on stronger footing as it faces a warmer-than-normal summer.

The settlement calls for Talen’s generators to bid into PJM’s capacity market, with any revenues to offset customer costs.
One area where many stakeholders find agreement on co-location policies – the need for clearer rules from PJM.

Rehearing requests were denied for plan to accelerate grid connection for shovel-ready projects, despite concerns from clean energy sector.

MISO’s proposed changes aim to enhance market protections against manipulation and fraud through stricter standards for demand response resources.

MISO’s proposed reforms impact an estimated 12 GW of demand response and emergency resources, most of which act as the final safeguard against involuntary load shedding.

The new process aims to accelerate the study of generation projects critical for grid reliability, as MISO faces a capacity shortfall that could grow to 4.7 GW by 2028.

FERC’s ruling affirms MISO’s discretion in how rules are set for measuring resources’ contributions to grid reliability, paving the way for implementation starting in the 2028/2029 planning year.

The proposal, the first change in PJM’s deactivation process in two decades, aims to improve grid reliability planning by updating generator deactivation processes in the face of increasing plant closures.

The extraordinary measure by PJM to speed up generator interconnections comes as the grid manager faces a potential 10 GW capacity gap by the end of the decade.
Project proponents say the pipeline is necessary to handle the expected surge in natural gas demand during the upcoming heating season.

Potomac Economics Ltd., in comments filed with FERC on Dec. 11, urged FERC to overhaul its interconnection and rate policies as massive electricity loads increasingly cluster with power generators.